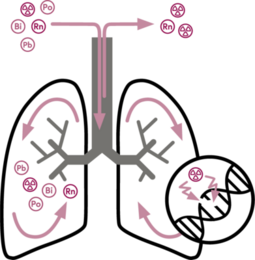
How does radon affect the lungs?
The radioactive noble gas radon and its by-products (lead, polonium and bismuth) enter the lungs when inhaled. As a gas, radon only remains in the airways for a short time and is quickly exhaled again. However, the radon by-products remain in the moist airways. They are also radioactive and have a short half-life, i.e. they lead to high radiation activity. When the radon progeny decay in the lungs, they emit radiation. This radiation can damage cells in the lung tissue and lead to lung cancer.
WHO classifies radon as a carcinogenic substance
The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies radon and its derivatives as proven carcinogens. Radon is therefore on the same level as tobacco smoke and asbestos. In Austria, radon is the largest contributor to the average radiation exposure of the population .
Radon is the most common cause of lung cancer after smoking! In people who have never smoked, radon is the most common cause of this type of cancer.
According to current knowledge, other health complaints are not caused by radon.